Lumbar Discopathy- Prophylaxis and Treatment
”I’m suffering from discopathy”- this statement is commonly associated with pain in the
lumbar spine region. What do we mean by ”discopathy’’, and what are the consequences?
There aren’t many people who can say they’ve never suffered from back pain. Intensive
lifestyle, desk job, lack of physical activity, bad eating habits- these are just a few of many
factors which cause quicker exploitation of our spine.
Unfortunately, degenerative changes in the spine region are unavoidable. The way we take
care of our ”main pillar” may define how soon the symptoms will occur.
WHAT IS DISCOPATHY?
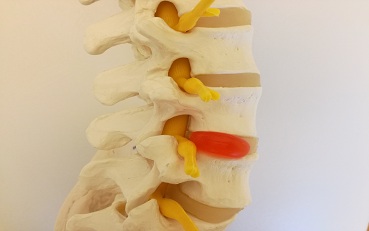
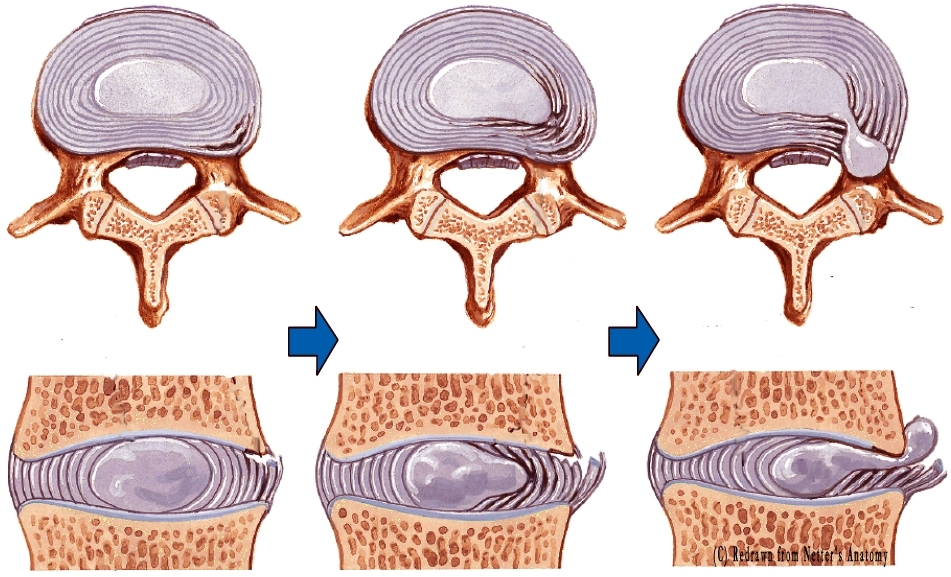
The intervertebral discs (known colloquially as discs) are structures made of connective tissue
with high water content (about 80%). Prolonged pressure on the discs leads to water
depletion, and consequently lowers their amortization abilities. As a result, it can cause a
rupture in their external layer, so called fibrotic ring, and migration of their inner structure
(a.k.a., nucleus pulposus). As soon as the process starts we can talk about discopathy, the next
stage begins with nucleus exiting outside the fibrotic ring.
”MY DISC SLIPPED, IT HAS TO BE REINSERTED ”
The foregoing phrase comes back to psychical therapists like a boomerang. We often hear
from patients that their disc slipped and it needs to be put back, reinserted, etc.
Of course, there is a certain movement between intervertebral disc and vertebral body, which
accounts for the mobility of spine. It is surrounded with strong ligaments and muscles, which
stabilize its position. However, there is no chance of disc moving far enough from spinal
column to actually called it ”slipped”. It is a colloquial expression and it is impossible to
”reinsert” the disc!
One of the treatment methods for discopathy is spinal manipulation, which is thought to be so
called ”adjustment”. After a detailed diagnose, a qualified physical therapist can perform a
swift movement that causes characteristic ”pop”. During this maneuver tissues surrounding
particular part of the spine relax, changing the pressure in joint capsule. This move often
brings instant relief and it is mistaken for ”sliding the disc back to its place”.
SYMPTOMS OF DISCOPATHY
Depending on the level of damage and severity of degenerative changes in the disc, as well as
other factors, symptoms of discopathy may vary. Individual approach and complete medical
history is vital for the proper spine assessment. Some of the most common symptoms of
discopathy include:
- Recurring pain in the lower part of the spine
- Morning ”stiffness”
- Acute pain exasperate by movement
- Pain in the buttocks area
- ”Girdling” pain in the lower part of the spine
- Numbness in the lower extremity (most commonly it starts with pain in the thigh area,
which may spread to the lower regions due to an intensified nerve root compression)
- Decreased muscle power in the lover extremity
- Foot drop- requires immediate medical attention
- Impaired control of masseter muscles- severe symptom, also requires medical attention
TREATMENT OF DISCOPATHY
”Prevention is better than cure"– excellent proverb which captures the essence of the spinal
disorders treatment. An intervertebral disc which has been damaged will be always prone to
further injuries, it can’t be fully restored.
That’s why it is so crucial to take care of our spine while it’s still healthy!
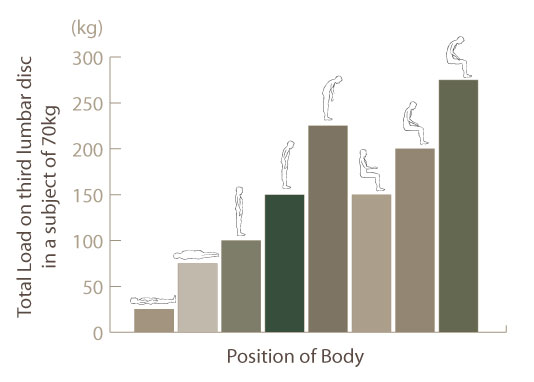
The main goal is to form movement habits which decompress the spine. The proper way to
lift heavy objects, the correct way of adjusting your posture while sitting at the desk and in a
car- those things should become our second nature and they increase our chances of spinal
longevity.
The most important element of prophylaxis are strong muscles which stabilize the spine.
Only regular exercises, which help to improve so called ”core stability”, can prevent
recurrence of symptoms. Some of which you can find HERE. However, in case of severe pain
we have to seek immediate medical attention. In the acute phase good method of treatment is
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication, which inhibits the process of inflammation and
edema, therefore relieving the pain. A common mistake in this phase is luck of any kind of
movement. ”It hurts when I move”. Unfortunately, it is a myth. Our spine needs movement in
order to support local blood supply and eliminate the swelling. ”What kind of movement is
safe for me?”. Each patient is different and so are the symptoms. That is why we should
immediately contact a physical therapist who will asses what kind of treatment is required.
This solution is far safer than taking advices from our colleague, neighbor or other
unqualified person! A specialist has to collect thorough medical history (find the cause of
pain); proper examination allows him to diagnose the patient and determine the course of
action. Discopathy is falsely perceived as a broad term that comprises all spine problems.
Individual approach allows us to choose the right course of treatment, thus ensuring a speedy
recovery!
If you feel any kind of spine related discomfort, or your seeking properly selected
exercises to strengthen it, be sure to visit us at CORE and MORE!